Why Choose Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Fracture Treatment?
The treatment of tibial fractures remains a challenge in orthopedic surgery. According to the Journal of Orthopedic Research, approximately 30% of all bone fractures occur in the tibia. This statistic highlights the need for effective treatment methods. The Tibial Interlocking Nail presents a promising solution for stabilizing these complex injuries. This method not only enhances the healing process but also reduces complications associated with traditional casts.
In recent studies, the success rate of Tibial Interlocking Nails reached over 90%. This is impressive compared to previous fixation methods. However, it is essential to recognize that not all cases lead to optimal outcomes. Some complications, such as infection or malunion, can still arise. Furthermore, patient factors significantly influence recovery times and overall results.
Many orthopedic surgeons are shifting toward the Tibial Interlocking Nail due to its advantages. It provides strong internal fixation and allows for early mobilization. Yet, careful patient selection is crucial. Understanding individual conditions can make a difference in recovery. This highlights the importance of ongoing research and training in the orthopedic field.
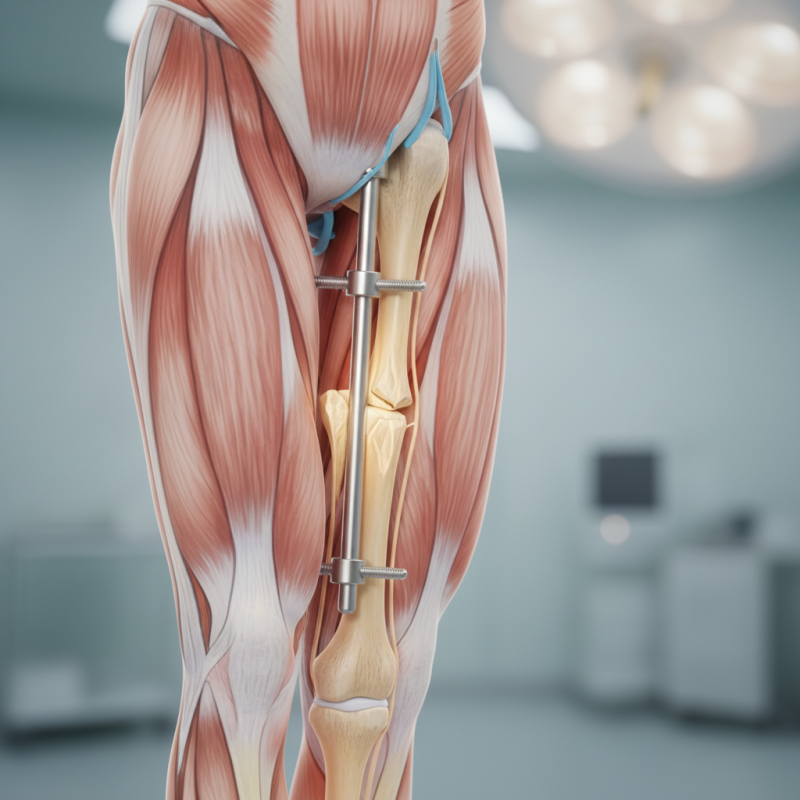
Advantages of Tibial Interlocking Nails in Fracture Management
Tibial interlocking nails have become a popular choice in fracture management. Their unique design allows for enhanced stability. The interlocking mechanism secures the nail in place, minimizing movement at the fracture site. As a result, patients often experience improved healing times.
One of the primary advantages of using tibial interlocking nails is their ability to support complex fractures. They are particularly effective in cases where traditional casting fails. Surgeons appreciate the versatility of this method. It can be used for a variety of fracture types. Yet, the surgery is not without risks. Infection or malalignment may occur, requiring further intervention.
Patient recovery varies. While many heal quickly, some face challenges. Adherence to rehabilitation protocols is crucial. Physical therapy plays a vital role in regaining strength and mobility. The journey might be tough, but many find it rewarding. The benefits of tibial interlocking nails often outweigh the potential drawbacks, making them a compelling option for fracture treatment.
Advantages of Tibial Interlocking Nails in Fracture Management
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails in Bone Fractures
Tibial interlocking nails are increasingly used in the treatment of bone fractures, particularly in the tibia. These nails are ideal for various fracture types, such as diaphyseal and metaphyseal fractures. A study published in the "Journal of Orthopedic Surgery" indicates a 90% success rate in alignment restoration with this method. Patients benefit from the stability provided by interlocking nails, reducing recovery time significantly.
In particular, complex fractures and those involving significant displacement can be effectively managed with tibial interlocking nails. These cases are often challenging and traditional methods may not yield optimal outcomes. Well-placed nails allow for weight-bearing sooner, aiding faster rehabilitation. However, improper insertion can lead to complications, such as malunion or infections. Attention to detail in placement is critical.
Tips: Always assess the patient’s overall health before opting for this approach. Monitor for signs of complications post-surgery. Effective rehabilitation is essential. Start gradual weight-bearing as guided by a professional. This method introduces flexibility in treatment options but may not be suitable for everyone. Regular follow-up is necessary to ensure optimal healing.
The Surgical Procedure for Tibial Interlocking Nail Placement
The surgical procedure for tibial interlocking nail placement begins with a thorough evaluation. The surgeon examines the fracture and plans the approach. A small incision is made on the skin over the bone. This is where the nail will be inserted. The area is then carefully isolated to ensure visibility.
Next, the surgeon uses a drill to create an entry point in the tibia. This step requires precision. The interlocking nail is then introduced into the bone. The surgeon checks alignment continuously. It’s important that the nail fits snugly but not too tight. Sometimes, adjustments are needed during the process.
After the nail is positioned, locking screws are inserted. This locks the nail in place, providing stability. X-rays are often taken at this stage to confirm proper placement. The incision is then closed in layers. Recovery begins shortly after the operation. Patients may experience discomfort and swelling, which is normal. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor healing. This procedure can be effective, but it’s not without challenges. Surgeons reflect on their experiences to improve techniques continuously.
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation After Nail Surgery
Post-operative care and rehabilitation after tibial interlocking nail surgery are crucial for optimal recovery. After the procedure, weight-bearing is generally restricted for about 6 to 12 weeks. This conservative approach helps to ensure proper healing and reduces the risk of complications. Physical therapy may be initiated early, focusing on range of motion and muscle strength. Studies show that early rehabilitation can lead to better functional outcomes.
Tips: Begin gentle exercises while adhering to the surgeon's guidelines. This can help improve circulation and decrease stiffness.
Patients often face challenges such as pain management and emotional adjustments. It's not uncommon to experience frustration during recovery. Engaging in supportive activities, like joining a recovery group, can provide motivation and help in coping with emotional hurdles. A 2021 study indicated that up to 30% of patients report anxiety surrounding the recovery process.
Tips: Keep a journal to express your thoughts and track your progress. This can be beneficial for mental health.
Every person's recovery timeline is unique. Many factors affect healing, including age, overall health, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Remember, it's okay to have setbacks. Recognize that healing takes time, and be patient with yourself as you navigate this journey.
Comparative Analysis of Tibial Interlocking Nails and Other Fixation Methods
Tibial interlocking nails are increasingly chosen for treating bone fractures. They stand out due to their unique design and functionality. Compared to plates or external fixators, these nails provide better stability. This option is less invasive, which means reduced soft tissue damage and quicker recovery times.
While interlocking nails have many benefits, they are not without challenges. Proper nail length and diameter selection is paramount. Surgeons must adapt to individual patient anatomy. Some patients may experience discomfort during the healing phase, which can be disheartening. Regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor progress and make adjustments.
**Tips:** Always communicate openly with your healthcare provider. Discuss any concerns about pain or limitations in movement. Adhere to rehabilitation protocols for optimal recovery. It's essential to stay informed about your treatment options. Each method has its pros and cons, so weigh them carefully.
Why Choose Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Fracture Treatment? - Comparative Analysis of Tibial Interlocking Nails and Other Fixation Methods
| Fixation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Indications | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibial Interlocking Nail | Minimal invasiveness, stability, early weight-bearing | Risk of infection, need for proper alignment | Comminuted fractures, intramedullary fixation | 6-12 weeks |
| Plate Osteosynthesis | Direct visualization, good alignment | Higher soft tissue dissection, longer surgery | Simple fractures, complex fractures requiring fixation | 8-16 weeks |
| External Fixation | Less soft tissue damage, adjustable | Uncomfortable for the patient, risk of pin site infection | Open fractures, limb shortening | 4-10 weeks |
| Intramedullary Nail (non-interlocking) | Simplicity in insertion, good rotational stability | Limited fracture types, less rigid fixation | Simple diaphyseal fractures | 6-12 weeks |
